Vital Signs: Human papillomavirus vaccine is cancer prevention
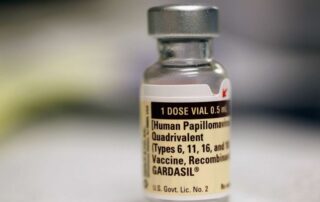
Author: Brenna Robertson Source: www.dailyprogress.com In a world of pandemics, vaccines, tests, and what feel like new threats to our health and safety every day, it is sometimes important to look back and review the basics of our personal health. This is particularly applicable when we think of infections that very easily spread from person to person. One such infection is the human papillomavirus (HPV). What is HPV? HPV, or human papillomavirus, is a group of more than 200 viruses, some of which can cause cancers, including cervical, oropharyngeal and anal cancer. About 75% of HPV-type viruses can cause warts or papillomas (non-cancerous tumors), while the other 25% affect mucosal areas such as the vagina, penis, anus and mouth. Although HPV causes more than 99% of cervical cancer cases, the CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention) states about 70% of oropharyngeal cancer is linked to HPV infections in the mouth and upper throat. Screening is important HPV impacts anyone of any gender, and anyone of any age can develop cancer after infection. It is so common, the CDC reports, that nearly everyone will get an HPV infection at some point in life. Because the virus can go undetected, it can put people at risk of developing cancer or unknowingly spreading the infection. The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that women start pap screenings at age 21. Early detection of oropharyngeal cancer is possible with routine mouth and upper throat screenings, so individuals should talk to their [...]